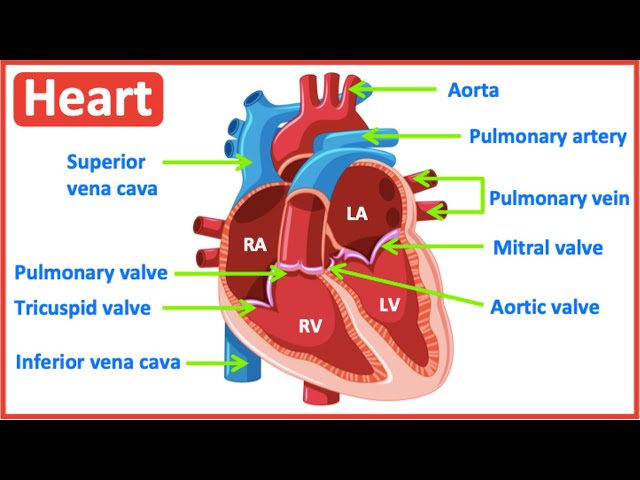
A heart labeled diagram is an invaluable tool for understanding the complex anatomy of the human heart. It provides a visual representation of the heart’s chambers, valves, major blood vessels, and their interconnections. This clarity is essential for medical students, healthcare professionals, and anyone seeking to improve their understanding of cardiovascular health. Such diagrams aid in the quick assimilation of complex information, making them crucial in educational and clinical settings. The precise labeling of each structure ensures accurate interpretation and avoids ambiguity. Ultimately, a well-constructed heart labeled diagram simplifies a sophisticated system.
Heart labeled diagrams offer a simplified, yet comprehensive overview of the cardiac anatomy. They are effective teaching aids in classrooms and hospitals, facilitating the understanding of intricate physiological processes. The visual nature of these diagrams aids in memorization and recall of crucial anatomical landmarks. Different diagrams may emphasize specific aspects, for example, blood flow or the electrical conduction system. The consistent use of standardized labeling conventions further enhances their utility and comprehension. They serve as a quick reference for professionals dealing with cardiac issues daily.
A well-designed diagram clarifies the relationships between different parts of the heart, thereby improving comprehension. Its visual nature enhances learning and retention compared to textual descriptions alone. For students, a heart labeled diagram aids in mastering fundamental concepts before proceeding to more advanced topics. For clinicians, it serves as a quick reference during diagnosis and treatment planning. The combination of visual cues and precise labels eliminates any potential ambiguity in identifying cardiac structures. A clear labeled diagram helps to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Understanding the Components of a Heart Labeled Diagram
Effective heart labeled diagrams typically illustrate the four chambers (right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle), the four major valves (tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic), and the major blood vessels (superior and inferior vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, aorta). The precise labeling of these components is critical for accuracy. These diagrams often use different colors to distinguish oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, further enhancing comprehension. The inclusion of a key or legend ensures clarity. Detailed diagrams may also illustrate the coronary arteries and the conduction system, crucial for understanding cardiac function and dysfunction.
The level of detail included in a heart labeled diagram varies depending on its intended purpose. A simple diagram might only show the major chambers and vessels, while a more complex one could include smaller branches of arteries and veins, along with the intricate network of the conduction system. The choice of diagram depends on the specific learning objectives or clinical needs. Regardless of the level of detail, accuracy and clear labeling are paramount. Consistency in terminology and symbols further improves understanding across different resources.
-
Step 1: Outline the Heart Shape:
Begin by sketching the basic shape of the heart, keeping in mind its overall proportions and the relative positions of the chambers. Consider using light pencil strokes for easy correction. Reference anatomical illustrations or photographs to guide the outline. Ensure the shape reflects the heart’s typical orientation within the chest cavity. Maintain a balanced and anatomically accurate representation.
-
Step 2: Divide into Chambers:
Divide the heart into its four chambers (right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle), paying close attention to their relative sizes and locations. Ensure accuracy in depicting the interventricular septum and the interatrial septum. Consider using dashed lines initially, which can be refined later. Refer to medical textbooks or reputable online resources for precise anatomical details.
-
Step 3: Illustrate Valves and Vessels:
Draw the major valves (tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic) and blood vessels (vena cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, aorta). Pay close attention to the direction of blood flow through each structure. Use arrows to clearly indicate the flow path. Ensure correct placement and anatomical relationships between the valves and chambers.
-
Step 4: Add Labels:
Carefully label each structure using clear, concise terminology. Ensure that labels are positioned to avoid obstructing the diagram’s overall clarity. Use a consistent font size and style. Avoid overlapping labels. A key or legend can be used to clarify abbreviations or symbols.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heart Labeled Diagrams
Heart labeled diagrams are frequently used in various educational and clinical settings, and many questions naturally arise regarding their construction, interpretation, and applications. Understanding the nuances of these diagrams is crucial for correctly interpreting the cardiovascular anatomy. A comprehensive approach to learning and using labeled diagrams enhances comprehension and retention of information. The clarity and accuracy of these diagrams impact their effectiveness in conveying complex anatomical information. Proper utilization of these diagrams leads to improved understanding of cardiac structure and function.
What are the key benefits of using a heart labeled diagram?
Heart labeled diagrams offer several key advantages. Primarily, they provide a visually clear representation of the complex anatomy of the heart, facilitating better understanding and memorization compared to textual descriptions alone. They are especially useful for educational purposes, helping students grasp the relationships between different heart structures. Furthermore, they serve as effective communication tools in clinical settings, enabling doctors and other healthcare professionals to explain cardiac conditions and procedures more effectively to patients. The visual nature of these diagrams improves patient comprehension and reduces anxiety. Finally, heart labeled diagrams are a valuable tool for self-learning, enabling individuals to explore the heart’s anatomy at their own pace. The combination of visual clarity and precise labeling makes them an invaluable resource.
How can I create an accurate heart labeled diagram?
Creating an accurate heart labeled diagram involves careful attention to detail and anatomical accuracy. Start by referring to reliable anatomical sources, such as medical textbooks or reputable online resources. Next, sketch the basic outline of the heart, followed by the chambers, valves, and major blood vessels. Use clear and concise labels, ensuring that each structure is correctly identified. Pay attention to the direction of blood flow, using arrows to indicate its path. Finally, review the finished diagram to ensure accuracy and clarity. Consistency in labeling and the use of a legend further enhance the diagram’s effectiveness. Consult medical illustrations for guidance and maintain consistency with established anatomical terminology.
Key Aspects of a Heart Labeled Diagram
A well-constructed heart labeled diagram is characterized by several essential aspects that impact its clarity and usefulness. These crucial elements combine to create a comprehensive and effective tool for understanding the cardiovascular system. Attention to detail and accuracy in the representation of anatomical structures are critical for proper interpretation. The accessibility and ease of understanding are equally important considerations in designing these diagrams. These aspects contribute to a significant improvement in both comprehension and retention of the information presented.
Accuracy
Accuracy is paramount; every structure must be precisely depicted and labeled. Inaccurate representation can lead to misunderstanding and misinterpretation of cardiovascular function. Reference reliable anatomical sources to ensure accuracy. Cross-referencing different sources strengthens the accuracy of the representation. The accuracy of the depiction directly influences the learning and comprehension processes. Even minor inaccuracies can propagate significant misunderstandings.
Clarity
Clarity is essential for ease of understanding. The diagram should be uncluttered and easy to interpret. Avoid overlapping labels or confusing lines. Use clear and legible fonts. A consistent color scheme can be used to differentiate structures or blood flow. Clarity helps improve comprehension and reduces ambiguity. Well-placed labels and appropriate use of color are both significant factors.
Labeling
Precise labeling is crucial for identification. Use standardized anatomical terminology. A legend can help clarify any abbreviations or symbols. Maintain consistency in the style and size of labels for improved readability. Clarity in labeling is pivotal for facilitating understanding. Precise anatomical terminology is a cornerstone of accurate representation.
Structure
The structural representation of the heart and its components is vital. The relationships between the chambers, valves, and blood vessels must be accurate and clearly shown. Proportional representation of different structures is important. Correct portrayal of the spatial relationships helps comprehension and prevents misinterpretation. It facilitates a clear and accurate understanding of the anatomical arrangement.
The combined impact of these key aspects ensures that the diagram serves its purpose effectively. These components work in synergy to convey complex information in a simplified and readily accessible format. The effectiveness of the diagram hinges on the successful integration of these essential elements. A well-executed diagram enhances learning, teaching, and clinical communication.
Effective utilization of a heart labeled diagram necessitates careful consideration of its design and interpretation. Understanding the underlying principles of anatomy is essential to appropriately utilize these diagrams. The accessibility of the diagram to the intended audience must also be factored in to optimize the learning process. A well-designed diagram serves as a critical tool for enhancing knowledge and understanding of the heart’s complex structures.
Tips for Using a Heart Labeled Diagram
To maximize the benefits of a heart labeled diagram, consider these tips. Understanding the diagram’s purpose and its intended audience is essential. The selection of a suitable diagram depends greatly on the specific needs. Appropriate use significantly enhances learning and comprehension. A well-chosen and effectively used diagram is a powerful teaching tool.
Start by identifying the key anatomical structures that need to be understood. Compare and contrast different diagrams to gain a comprehensive understanding. Engage actively with the diagram, tracing blood flow and identifying relationships between structures. Relate the diagram to real-world scenarios such as cardiac conditions or surgical procedures. Use the diagram as a reference tool while reading related materials.
-
Trace Blood Flow:
Follow the pathway of blood through the heart, starting from the vena cavae and ending at the aorta. This helps to understand the circulatory system’s mechanics. Focus on the direction of flow and the role of each valve. Understanding this flow helps in grasping the heart’s function. This active engagement enhances learning and retention.
-
Relate to Function:
Connect the anatomical structures to their physiological functions. Understanding how each chamber and valve contributes to the heart’s overall function is crucial. Consider how the structures interact to regulate blood flow. This integration of structure and function deepens comprehension.
-
Compare and Contrast:
Compare multiple diagrams to identify similarities and differences in representation. This strengthens the understanding of the heart’s anatomy. Different diagrams may emphasize different aspects of the heart. This comparative approach enhances learning and understanding.
-
Use as a Reference:
Consult the diagram while studying related texts or videos. This helps to visually reinforce concepts. The diagram complements textual descriptions and visual aids. It serves as a handy reference throughout the learning process.
-
Relate to Clinical Cases:
If studying clinical scenarios, use the diagram to visualize the location of the affected structures. It helps understand the impact of specific conditions. Clinical relevance significantly enhances learning. This integration of theory and practice strengthens knowledge.
Heart labeled diagrams serve as excellent visual aids in the learning process. Their use complements textual and other forms of learning. Understanding the heart’s intricate structure is significantly aided by these visual aids. Proper use of a heart labeled diagram significantly enhances the overall learning experience.
The ability to accurately interpret and apply knowledge from a heart labeled diagram is a valuable skill. These diagrams are tools for improving understanding of complex cardiovascular anatomy. Proficiency with this tool is beneficial for both students and healthcare professionals alike. Effective use of these diagrams aids in understanding the heart and improving medical practice.
In conclusion, the effective use of a heart labeled diagram is crucial for comprehending the complexities of cardiac anatomy and physiology. Its application extends beyond educational settings, proving vital in healthcare for diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient education. A heart labeled diagram serves as a powerful tool for fostering a deeper understanding of this vital organ.
Youtube Video: